Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending 2025 – How It Works, Risks & Returns
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending connects borrowers with investors through online platforms, bypassing traditional financial institutions. Borrowers gain access to alternative financing and easier loan approval, while investors earn higher returns. Peer-to-peer lending lets retail investors fund consumer & SME loans online. The global market hit $210 bn in 2023 and is growing 25 %+ CAGR, but default, liquidity and platform-failure risks remain.[1]

What is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending is an innovative form of borrowing and investing money without the involvement of traditional financial institutions. By using online platforms, borrowers and lenders can make mutually beneficial transactions directly without the need for a bank as a middleman.
P2P lending is a type of crowdfunding investment also known as "social lending", "debt-based crowdfunding", or "crowdlending". With more than 100 peer-to-peer lending websites operating worldwide, the market has experienced tremendous growth in recent years. The most popular sites in the world, such as Lending Club, Prosper, and Funding Circle, were early adopters. In recent years, they have either transitioned into banks or closed their doors to retail investors.
How Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending Works
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending works as private credit by connecting borrowers who need money with lenders who want to make a return on their investments. Borrowers submit loan requests to the peer-to-peer lender and investors then compete to finance the loans in exchange for an interest rate. From start to finish, P2P sites manage the entire process, including rating creditworthiness, loan servicing, payments, and collections.
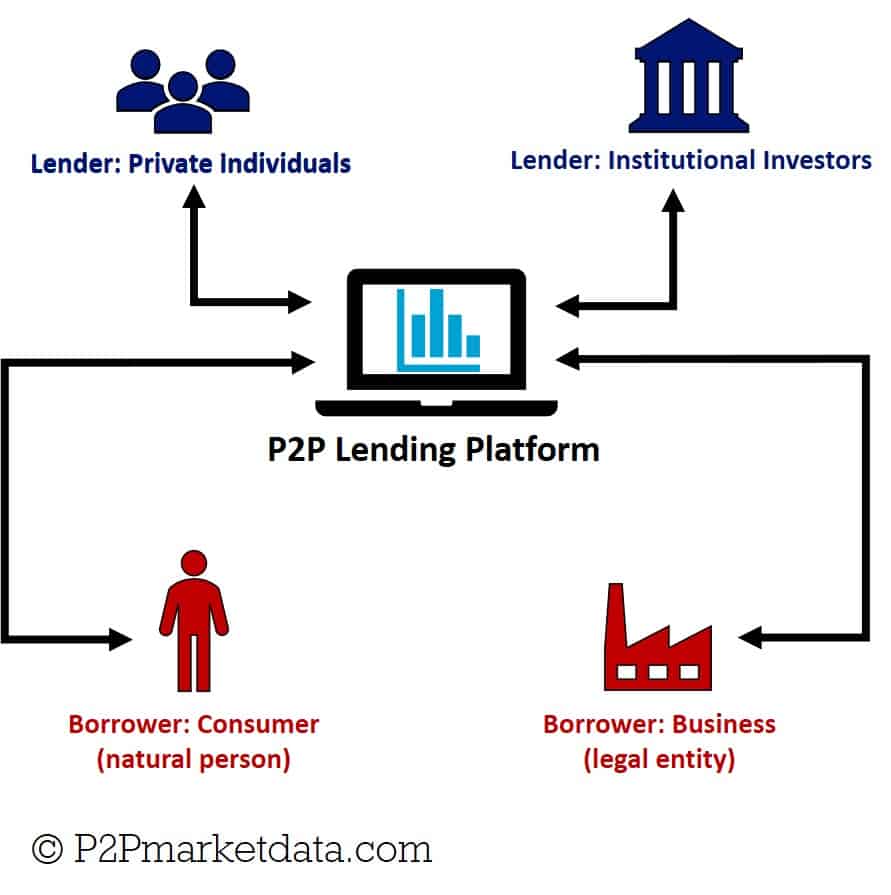
At first, an investor creates a profile on the website and transfers funds that will be distributed in loans. A loan applicant submits their financial information which receives a risk rating. This then determines the rate of interest the borrower has to pay. Peer-to-peer lenders can then select from different loan offers and choose the ones they deem to have an acceptable risk-reward ratio. Once the loans are funded, interest payments start being made as soon as the borrowers repay their debt according to schedule. The peer-to-peer lending website handles the disbursement of funds and the collection of loan payments. All transactions happen on a private market without the involvement of banks or hedge funds.
So what makes peer-to-peer lending that different from balance sheet lending and traditional banks? Simply put, peer-to-peer lending is faster, more convenient, and easier to access than traditional bank loans. P2P lenders provide much more flexible borrowing terms because they don't have to adhere to the strict regulations imposed by banks.[2]
Types of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending Websites
Peer-to-peer lending can come in a variety of different models and types, including personal loans, business loans, student loans, and mortgage financing. Most sites specialize in one or two specific types of borrowers.
Personal loans are the most common type of loan offered via peer-to-peer platforms. These types of loans are unsecured and usually range from $1,000 to $25,000 with a repayment period of up to 5 years. Business loans are also offered through P2P lending sites, ranging from $50,000 to $500,000 with flexible repayment options. The two most popular sites in the world, Lending Club and Prosper are two examples of the most common types of peer-to-peer lending.
- Lending Club is a peer-to-peer lending platform that allows borrowers to apply for personal and small business loans in the USA. With these loans, investors can conveniently secure a return of up to 3.65% from their Savings Account. In recent years Lending Club has transitioned into a bank and closed for retail investors.[3]
- Prosper is another popular peer-to-peer lending platform, offering unsecured personal loans of up to $50,000 with competitive interest rates for American citizens. Investors can individually purchase notes backed by these loans with minimal fees and a relatively low minimum investment requirement.[4]
Stepping away from traditional bank loans, peer-to-peer lending sites provide solutions that banks may be too expensive or slow-moving to offer, like real estate development loans, small business loans, and invoice financing. The peer-to-peer lending market is constantly expanding and now provides an array of innovative financial products far exceeding personal loans to renewable energy loans, real estate crowdfunding, farming and machinery credit options, a so-called buyback guarantee, and even lawsuit loans.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending Investing
The simplest way to invest in peer-to-peer lending is to register with a P2P lending website and start selecting borrowers. As a peer-to-peer lender, you usually have the opportunity to choose borrowers based on factors like their credit score and interest rate. You can decide if you want to pursue high potential returns but more risk or lower returns with safer collateral. With certain P2P lending sites being public companies, you can also invest in them through the public stock market or by participating in early-stage funding rounds on startup investment sites.
For investors, peer-to-peer lending offers a new way to diversify their portfolios and explore alternative investments with attractive returns. Investing in P2P loans is becoming increasingly popular among those who understand how to analyze risks and secure higher returns from their investments.[5] With the right platform, peer-to-peer lending can provide an attractive addition to many investors' portfolios.
Peer-to-Peer Lending Tips
People who are looking to invest in peer-to-peer lending should be aware that borrowers do default on their loans, and the degree of supervision and oversight of P2P lending sites differs from country to country. P2P lending scams are an unfortunate reality in the modern age of digital banking and investments. Whenever you loan money to someone, there's always a risk of getting scammed or swindled, and peer-to-peer lending is no exception.[6]
Robert G. Wilmers, the esteemed Chairman and CEO of M&T Bank, once said, 'The only good loan is one that gets paid back.' This timeless advice is especially relevant in the world of peer-to-peer lending, where evaluating risk and ensuring repayment are critical to success. Whether you're a seasoned lender or just starting out, keeping this principle in mind can help guide sound investment decisions.
The only good loan is one that gets paid back
Research suggests that because of the lack of industry-wide transparency regarding past and existing loan performance, some platforms are incentivized to use models that exaggerate their internal rate of return. As a result, some p2p lending sites might display returns higher than those actually seen when accounting for defaults.[7]
P2P lending sites generate revenue from transaction fees that can be imposed on the borrower, lender, or both. Anyone investing or looking to borrow money with peer-to-peer lending should pay attention to any fees that may apply. Every website has different fees and commissions, which can range anywhere from withdrawal costs to currency exchanges, origination charges, or servicing charges to late payment penalties.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending offers investors the potential for higher returns and the opportunity to diversify their portfolios. However, it comes with risks such as borrower defaults and limited regulation, with few options for recourse if repayments are not made. Let’s explore the key advantages and disadvantages for investors in peer-to-peer lending.
Advantages
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending offers investors higher returns, portfolio diversification, and access to alternative investments. With greater control and flexibility, it’s an attractive option for those seeking competitive returns and a unique asset class in today’s financial market.
Disadvantages
While peer-to-peer (P2P) lending offers compelling opportunities, it also comes with significant risks that investors should carefully consider. The disadvantages of P2P lending, such as credit risk, lack of liquidity, platform instability, and limited protection, highlight the importance of thorough research and risk management. Understanding these challenges is essential for making informed decisions and mitigating potential losses in this alternative investment space.
Is peer-to-peer lending regulated?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending regulations vary significantly across regions, reflecting different approaches to investor protection, platform accountability, and market operation. In the United States, United Kingdom, and European Union, distinct regulatory frameworks shape the way platforms operate and how investors engage. Understanding these regional regulations is crucial for navigating the complexities of P2P lending and ensuring compliance while minimizing risks.
- European Union: P2P lending in Europe is regulated under the EU Crowdfunding Regulation, which requires platforms to be licensed as Crowdfunding Service Providers (CSPs). It establishes a unified framework across member states, includes investor protections, and mandates KYC checks.
- United States: P2P lending in the U.S. is regulated by federal bodies like the SEC, which oversees the investment side, and the CFPB and FTC, which protect consumers. States add further regulations, creating compliance challenges. Platforms partner with banks to issue loans and securities, meaning lenders are creditors of the platform. The market mainly focuses on consumer loans.
- United Kingdom: P2P lending in the UK is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Platforms must be FCA-authorized, and consumer protections include a 10% investment limit for retail investors and transparency on risks. P2P investments aren’t covered by the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), and investors could lose their money if a company or platform fails.
What is the difference between crowdfunding and peer-to-peer lending?
Peer-to-peer lending (also called debt-based crowdfunding) is a type of crowdfunding and in most of the world, it accounts for more than 80% of the money facilitated in crowdfunding every year. It differentiates from other types of crowdfunding such as donation- or reward-based crowdfunding by being fully based on loans between people compared to donations or products as rewards.
Are peer-to-peer loans more expensive than traditional banks?
It is common that P2P lending sites offer higher interest rates than conventional bank loans. The borrowers use peer-to-peer lending because they can either get a loan fast or because p2p lenders are more willing to provide financing to less creditworthy or unique borrowers than banks. There are also other benefits such as acquiring mini-ambassadors (crowd of potential customers), support in terms of unique business knowledge, or simply because they can get better payment terms in regards to interest, duration, or type of loan.
Thanks to its public and transparent nature, borrowers are granted the ability to compare loan terms to other already funded participants in the open peer-to-peer lending market – something which is not available in traditional banking practices where information remains hidden from view.
What happens if you don't pay back a peer-to-peer loan?
If the borrower does not pay back the loan, the lender has the legal right to take action. This is why peer-to-peer websites usually require collateral, such as property or other assets, in case of default. The peer-to-peer lending website usually acts as a debt collection agency but also sometimes hires external collectors to recover any losses for the investors.
It is important to note that peer-to-peer lending platforms often have their own terms and conditions for defaults and late payments. Borrowers and investors should be sure to thoroughly read these before entering into any loan agreements as they may differ from platform to platform.
How do you qualify for a peer-to-peer loan?
To be eligible for a peer-to-peer loan, you must typically meet the platform's criteria. Most platforms seek potential borrowers with a minimum credit score or income level and often require them to provide some form of collateral as security. Each platform has different standards and guidelines, so it is essential to thoroughly read the terms of each before submitting a loan application.
For those who don't meet minimum requirements, some platforms provide co-signer loans - a solution that involves another person taking legal responsibility for loan repayment if you are unable to do so.
Peer-to-Peer Lending Analytics Tool
Are you a savvy investor on the hunt for lucrative returns through alternative investment platforms such as peer-to-peer (P2P) lending? It can be difficult to identify reliable and fruitful sites amongst the many peer-to-peer lending sites available. That's why P2PMarketData was created; we assist investors in their search by scrutinizing data from participating websites. Begin your journey into peer-to-peer lending by reading analyses of investment sites, or take a look at our broad library of alternative investments open for funding right now.
Article Sources
- GlobalMarketInsights: “Peer to Peer Lending Market”
- SpringerOpen: “Regulatory constraint and small business lending: do innovative peer-to-peer lenders have an advantage?”
- LendingClub: “How It Works”
- Prosper: “Personal Loans”
- PR Newswire: “Peer-to-Peer Lending Market to Gain Value of $ 1.14 Trillion by 2031, TMR Report”
- Crowdfund Insider: “What’s Going on With Peer to Peer Lender Grupeer?”
- SpringerOpen: “Default or profit scoring credit systems? Evidence from European and US peer-to-peer lending markets”